PRELIMINARY SCREENING OF GENE
EXPRESSION IN SCHIZOPHRENIA BY cDNA MICROARRAY
Marquis P. Vawter, University of
California at Irvine
Microarray studies can be used to
examine expression levels for large numbers of genes simultaneously, and may be
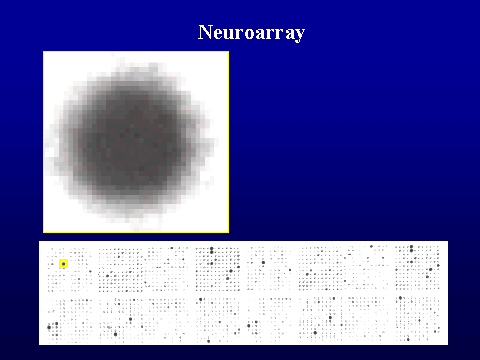
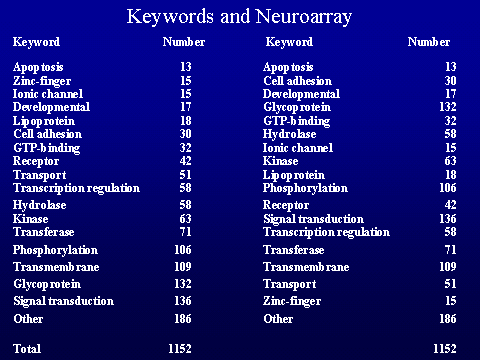
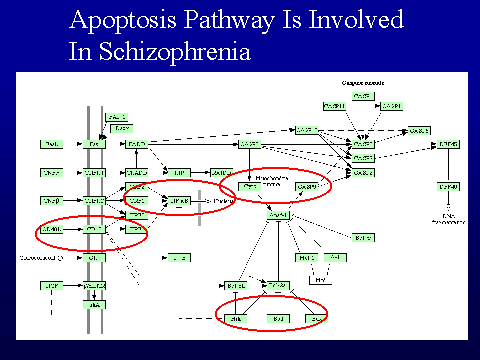
applied to identify genes involved in schizophrenia. A microarray with
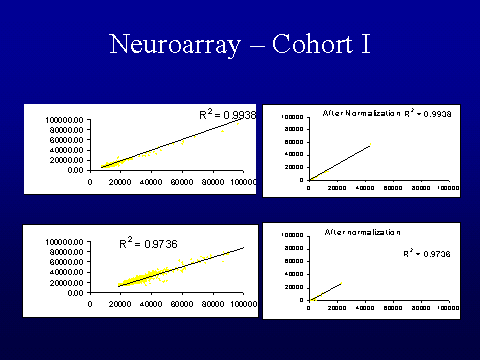
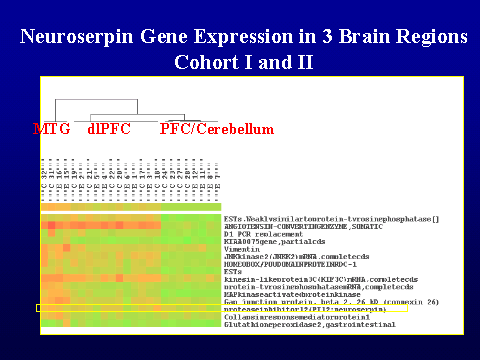
1127 brain-relevant genes was used to screen relative gene expression in total
RNA pools (Barrett et al, 2001). Pooling of tissue samples was employed,
as a strategy to detect changes in gene expression that are consistently found
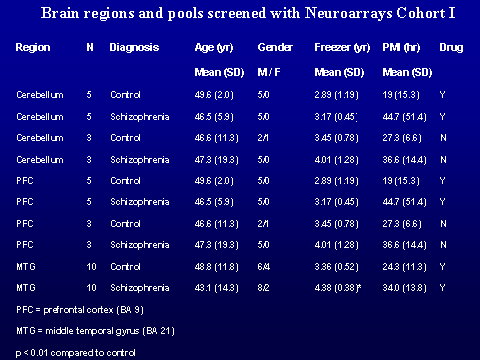
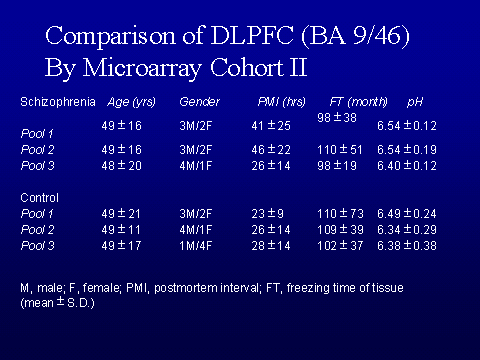
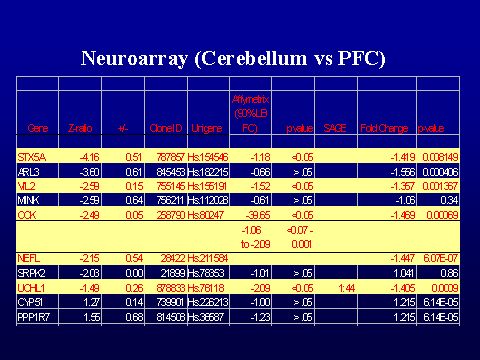
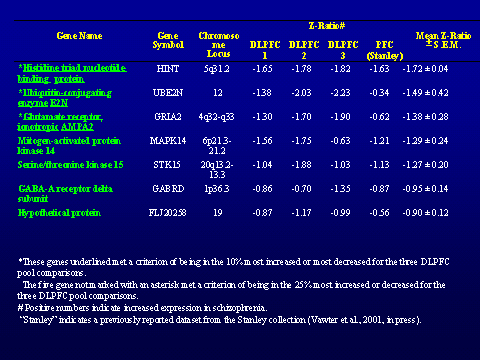
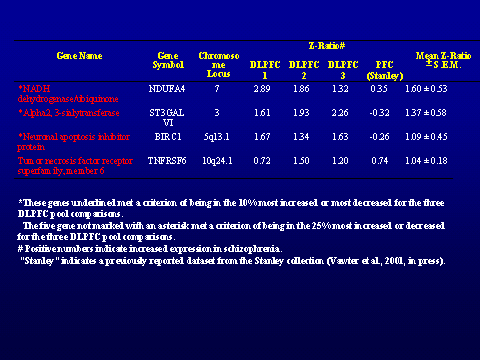
across individual cases of schizophrenia. The brain regions examined by
microarray were prefrontal cortex, cerebellum, and medial temporal gyrus in 8
pools of patients with schizophrenia and 8 matching control pools (Vawter et.
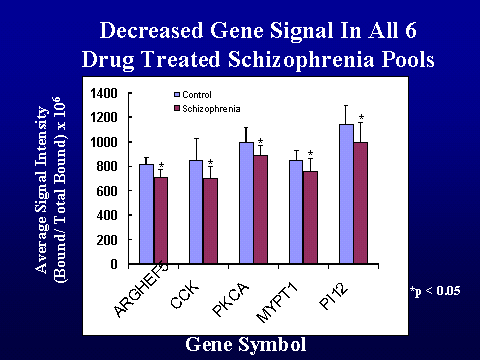
al, 2001; Vawter et al. in press). The data has been analyzed by comparing
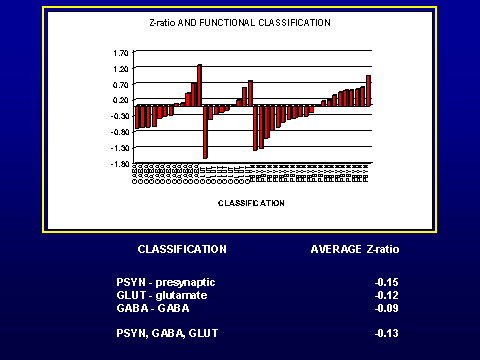
normalized ratios for each gene in schizophrenia pools to matched control pools
using Cyber-T (Long, et al, 2001). An analysis combining gene expression
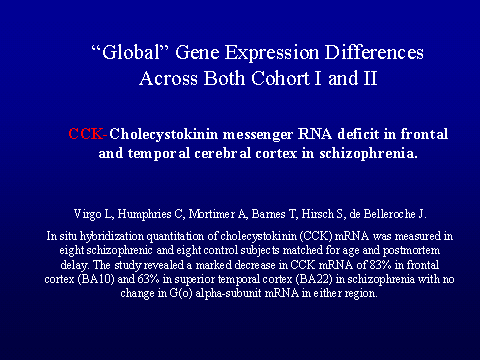
in all brain regions was conducted to examine possible global gene differences
between schizophrenia and control pools. The results of the regional and
global analysis will be presented. These results are subject to
limitations based on variations inherent to human subjects and tissue samples,
possible effects of neuroleptic treatment, and the requirement for verification
using independent techniques. We are currently examining individual gene
expression differences by independent verification methods.
Slides:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
